e. Setup monitoring
In this section, you will learn how to monitor your cluster and the pods running on it.
There are several ways to set up monitoring. You will walk through two approaches in order to learn about simple built-in command line-based monitoring as well as comprehensive graphical dashboard-based monitoring.
1. Monitor using kubectl
This method allows viewing of cluster-wide metrics in textual form.
1.1. Deploy metrics server
To enable utilization monitoring of the cluster using kubectl, deploy the Kubernetes metrics server by executing the following command:
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/metrics-server/releases/latest/download/components.yaml
Please allow 1 to 2 minutes for the metrics server to initialize, then proceed to the next step. If you execute the next step and see an error instead of the expected output, please wait a few more seconds and retry.
1.2. Execute kubectl
To see node utilization of your cluster, execute:
kubectl top node --use-protocol-buffers
Sample output:
NAME CPU(cores) CPU% MEMORY(bytes) MEMORY%
ip-192-168-86-187.ec2.internal 201m 0% 1362Mi 0%
To see how much resources each pod is utilizing, execute:
kubectl top pod -A --use-protocol-buffers
Sample output:
NAMESPACE NAME CPU(cores) MEMORY(bytes)
kube-system aws-node-crzgq 6m 83Mi
kube-system aws-node-qjx2h 4m 81Mi
kube-system coredns-f47955f89-dsrjp 3m 27Mi
kube-system coredns-f47955f89-vvvn4 3m 26Mi
kube-system fsx-csi-controller-78b5599496-2992k 9m 80Mi
kube-system fsx-csi-controller-78b5599496-5gf5k 5m 66Mi
kube-system fsx-csi-node-bxjzc 2m 53Mi
kube-system fsx-csi-node-qs9dh 8m 52Mi
kube-system kube-proxy-l6747 11m 52Mi
kube-system kube-proxy-ntjf7 13m 51Mi
kube-system metrics-server-64cf6869bd-b9lsg 5m 28Mi
2. Monitor using Prometheus and Grafana
This approach allows cluster-wide monitoring through a web-based graphical user interface.
2.1. Add helm repositories
Add the Prometheus and Grafana helm repositories by executing the following commands:
# add prometheus Helm repo
helm repo add prometheus-community https://prometheus-community.github.io/helm-charts
# add grafana Helm repo
helm repo add grafana https://grafana.github.io/helm-charts
2.2. Deploy Prometheus
The Prometheus server collects and exports cluster metrics. Execute the following commands to deploy it:
kubectl create namespace prometheus
helm install prometheus prometheus-community/prometheus \
--namespace prometheus \
--set alertmanager.persistentVolume.storageClass="gp2" \
--set server.persistentVolume.storageClass="gp2"
To verify the deployment, execute:
kubectl get all -n prometheus
The expected output looks similar to this:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/prometheus-alertmanager-6f64cb4659-wkbj5 2/2 Running 0 107m
pod/prometheus-kube-state-metrics-77ddf69b4-z8z4z 1/1 Running 0 107m
pod/prometheus-node-exporter-lm4rt 1/1 Running 0 107m
pod/prometheus-node-exporter-r4hbp 1/1 Running 0 107m
pod/prometheus-pushgateway-5f7dcb67bb-b4z5k 1/1 Running 0 107m
pod/prometheus-server-584d5c7c84-gmf4z 2/2 Running 0 107m
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/prometheus-alertmanager ClusterIP 10.100.15.106 <none> 80/TCP 107m
service/prometheus-kube-state-metrics ClusterIP 10.100.38.71 <none> 8080/TCP 107m
service/prometheus-node-exporter ClusterIP 10.100.28.205 <none> 9100/TCP 107m
service/prometheus-pushgateway ClusterIP 10.100.76.25 <none> 9091/TCP 107m
service/prometheus-server ClusterIP 10.100.103.56 <none> 80/TCP 107m
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE NODE SELECTOR AGE
daemonset.apps/prometheus-node-exporter 2 2 2 2 2 <none> 107m
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/prometheus-alertmanager 1/1 1 1 107m
deployment.apps/prometheus-kube-state-metrics 1/1 1 1 107m
deployment.apps/prometheus-pushgateway 1/1 1 1 107m
deployment.apps/prometheus-server 1/1 1 1 107m
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/prometheus-alertmanager-6f64cb4659 1 1 1 107m
replicaset.apps/prometheus-kube-state-metrics-77ddf69b4 1 1 1 107m
replicaset.apps/prometheus-pushgateway-5f7dcb67bb 1 1 1 107m
replicaset.apps/prometheus-server-584d5c7c84 1 1 1 107m
2.4. Deploy Grafana
The Grafana server displays metrics from Prometheus as graphical dashboards.
First create a data source manifest for Prometheus:
mkdir ${HOME}/environment/grafana
cat << EoF > ${HOME}/environment/grafana/prometheus.yaml
datasources:
datasources.yaml:
apiVersion: 1
datasources:
- name: Prometheus
type: prometheus
url: http://prometheus-server.prometheus.svc.cluster.local
access: proxy
isDefault: true
EoF
Deploy Grafana and configure it with Prometheus as the data source:
kubectl create namespace grafana
helm install grafana grafana/grafana \
--namespace grafana \
--set persistence.storageClassName="gp2" \
--set persistence.enabled=true \
--set adminPassword='SC22!sAWSome' \
--values ${HOME}/environment/grafana/prometheus.yaml \
--set service.type=LoadBalancer
To verify the deployment, execute:
kubectl get all -n grafana
The expected output looks similar to the following:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/grafana-7c4b6ccb8-q2qsv 1/1 Running 0 110m
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/grafana LoadBalancer 10.100.159.35 <pending> 80:31114/TCP 110m
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/grafana 1/1 1 1 110m
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/grafana-7c4b6ccb8 1 1 1 110m
2.5. Connect and login to Grafana
In a production deployment, Grafana would typically be exposed via an Application Load Balancer, configured with a domain name and an SSL certificate. For this lab we are using a classic lod balancer and traffic is over HTTP.
To get your Grafana URL, execute:
export LB=$(kubectl -n grafana get svc grafana -o json | jq -r .status.loadBalancer.ingress[].hostname)
echo "Your Grafana URL is:"
echo "http://${LB}"
Open the Grafana URL. It may take a few minutes for the Grafana URL to become active. When the load balancer is provisioned and its DNS record has propagated, you will see the Grafana login screen. Note that DNS record propagation may take about 5 minutes. Refresh the page periodically until you see the Grafana login.
Login as user admin
To obtain the password, execute the following command:
kubectl get secret --namespace grafana grafana -o jsonpath="{.data.admin-password}" | base64 --decode ; echo
2.6. Open dashboards
We will import two standard dashboards from Grafana.com
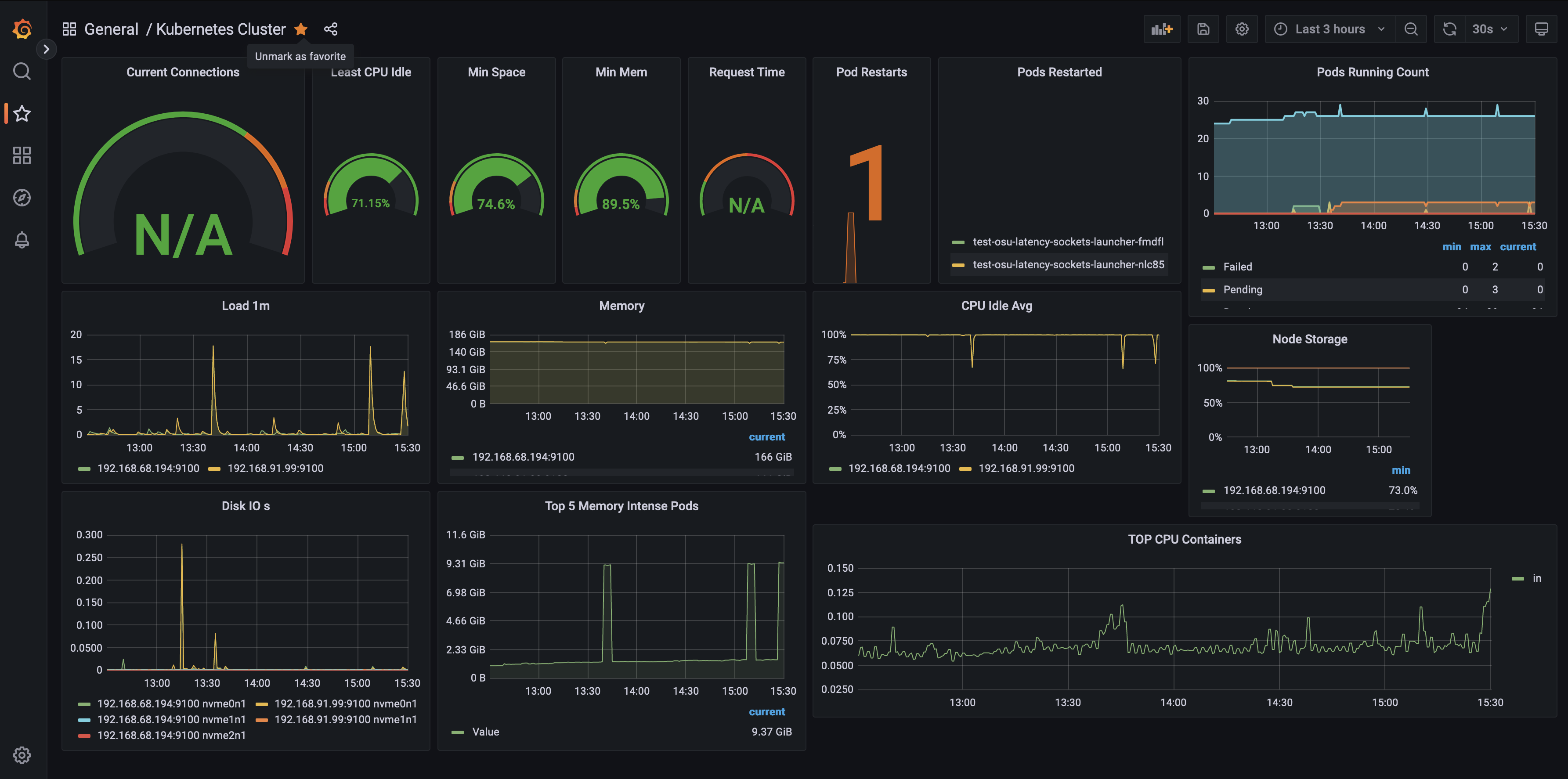
2.6.1. Cluster Monitoring Dashboard
- Click on Dashboards->Import
- Enter dashboard id
7249under Grafana.com Dashboard - Click ‘Load’
- Select ‘Prometheus’ as the endpoint under the “Prometheus data sources” drop down
- Click ‘Import’
You will see a Cluster monitoring dashboard similar to the one below:
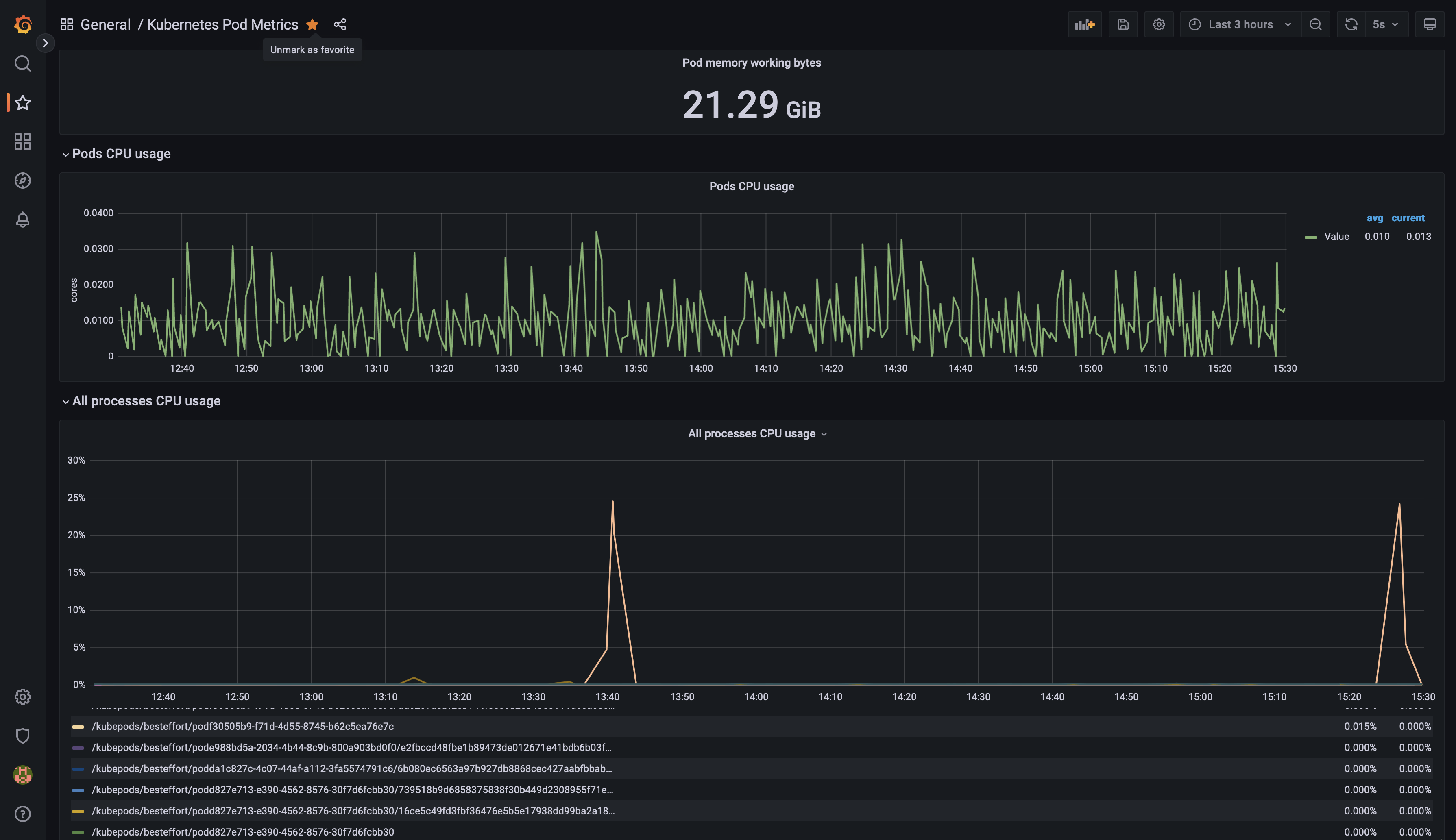
2.6.2. Pod Monitoring Dashboard
- Click on Dashboards->Import
- Enter dashboard id
747under Grafana.com Dashboard - Click ‘Load’
- Select ‘Prometheus’ as the endpoint under the “Prometheus data sources” drop down
- Click ‘Import’
You will see a Pod monitoring dashboard similar to the one below: